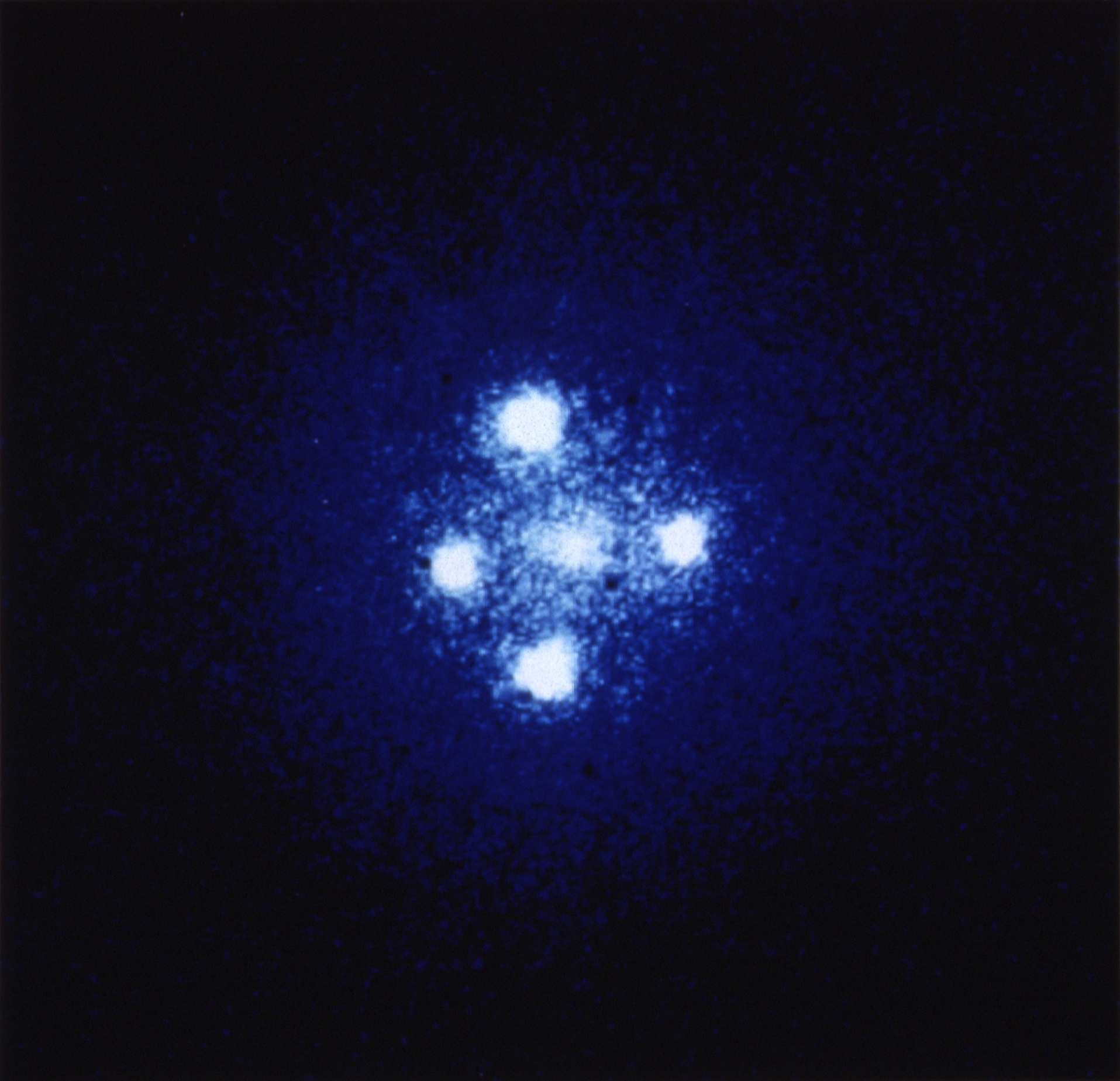
The Einstein cross
The Einstein cross
The above image shows 4 images of the same object gravitation-ally lensed by the central object. This shows the light taking 4 distinct paths through space-time from our frame of reference.
All wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation travel a straight line through space-time. Mass warps space-time so light passing by a galaxy, black hole or compact stellar object of mass M gets refracted by angle by the equation:.

The above image is an Einstein Ring which was a prediction made by Albert Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity.